Clinical Studies
There are two pivotal studies that show:
Cysview is clinically proven to detect bladder cancer that would be missed by White Light Cystoscopy alone.1
Study 11
- A prospective, multicenter, within-patient controlled, clinical trial in adult patients with known or suspected bladder cancer who were randomized to either White Light Cystoscopy (WLC) (control group, n=384) or WLC followed by Blue Light Cystoscopy (BLC) (study drug group, n=395).
- Only the study drug group patients received Cysview by bladder instillation prior to cystoscopy. After bladder evacuation of Cysview, bladder lesion mapping was performed initially using the KARL STORZ PDD system in the white-light mode followed by lesion mapping in the blue-light mode. Control group patients underwent only WLC with lesion mapping.
- The intention-to-treat (ITT) detection group, 286 patients, had at least one Ta and/or T1 lesion, including 47 patients who had additional tumors only found by BLC with Cysview.

Study 22
- A prospective, open-label, within-patient controlled, clinical trial using Blue Light Cystoscopy (BLC) with Cysview in the detection of bladder cancer during surveillance cystoscopy. Patients with bladder cancer in follow-up for tumor recurrence (n=304) received Cysview by bladder instillation.
- After bladder evacuation of Cysview, a standard White Light Cystoscopy (WLC) was performed, followed by BLC with Cysview using the KARL STORZ D-Light C Photodynamic Diagnostic (PDD) System with the Flexible PDD Videoscope System. Suspected malignant lesions were counted and evaluated.
- Patients with suspected recurrence (n=103), underwent a Cysview instillation followed by WLC and BLC with Cysview in the operating room (OR) using the KARL STORZ D-Light C PDD System with the Rigid PDD Cystoscope System. Lesion mapping was also done. The suspicious lesions were biopsied and surgically removed by TURBT.
- Of 63 patients with confirmed malignancy at TURBT, 13 (21%) were only found with Cysview.
- Of 26 patients with confirmed CIS, 9 (35%) patients were found only with Cysview.
- The study’s primary efficacy end point was the proportion of patients with histologically confirmed malignancy that was detected only by BLC and not by WLC in the surveillance setting.


Table of Results 1
| Bladder Tumor Detection within the Study Drug Group by WL and/or BL Cystoscopy1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of lesions | Detected by Both WL & BL | Detected by WL Only | Detected by BL Only |
| CIS, n = 66 | 33 | 6 | 27 |
| Ta, n = 580 | 472 | 52 | 56 |
| T1, n = 95 | 76 | 10 | 9 |
| T2 - T4, n = 47 | 38 | 8 | 1 |
| Among the lesions detected only by BL, 23% were negative for any carcinoma-related pathology, including dysplasia. Among the lesions detected by only WL, 17% were negative for any carcinoma-related pathology, including dysplasia. | |||
Adverse Events 1
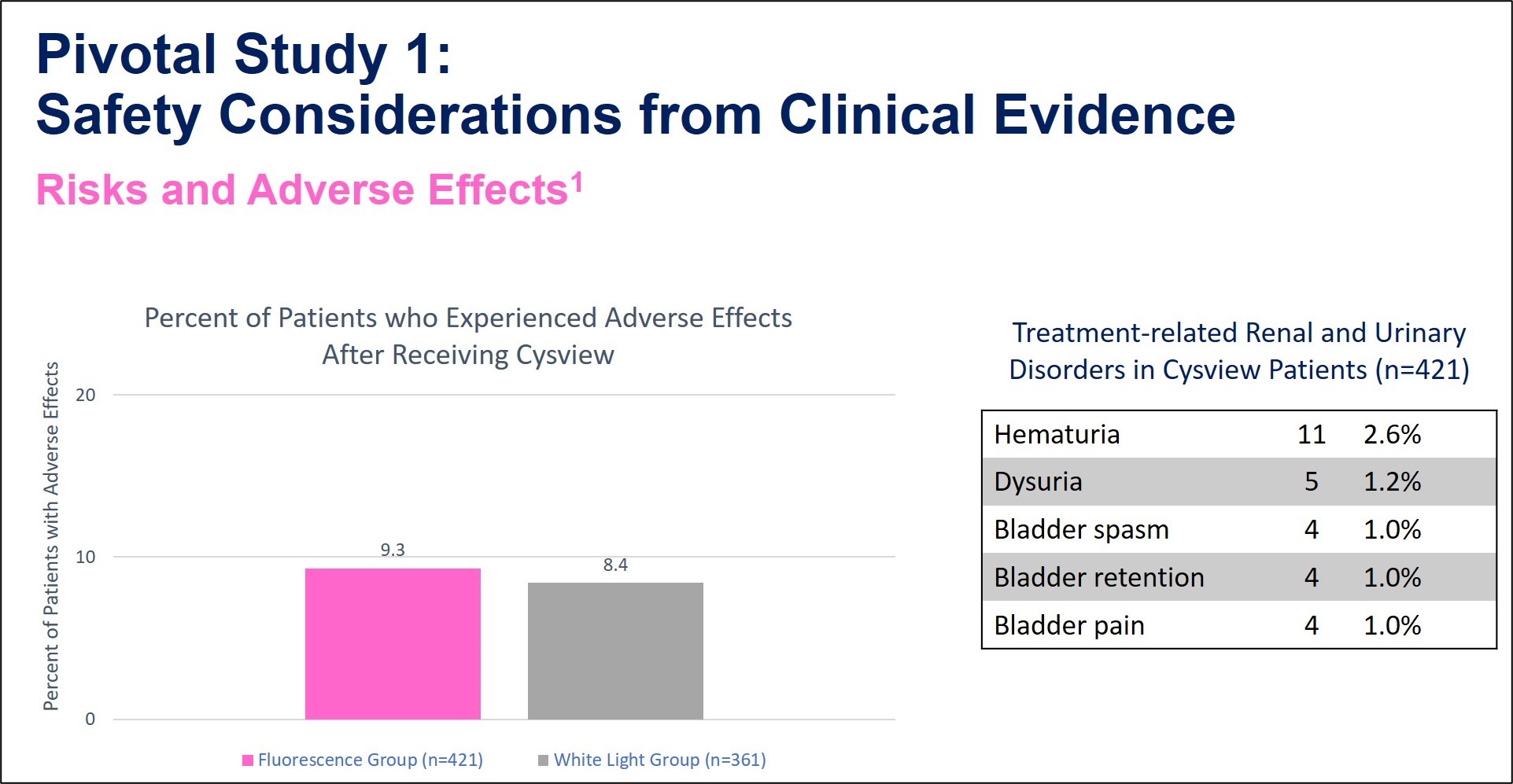
Table of Results 2
| Lesion Detection by Type of Malignancy as Verified in the OR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malignancy Type | Detected by Both WL & BL | Detected by WL Only | Detected by BL Only | |
| CIS, n = 43 | 24 | 3 | 16 | |
| Ta, n = 94 | 61 | 9 | 24 | |
| T1, n = 10 | 7 | 0 | 3 | |
| T2 - T4, n = 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | |
| PUNLMP** n = 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | |
| False positive n = 160 | 65 | 22 | 73 | |
| Total number of lesions | 164 | 34 | 117 | |
| ** papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential | ||||
Adverse Events 2
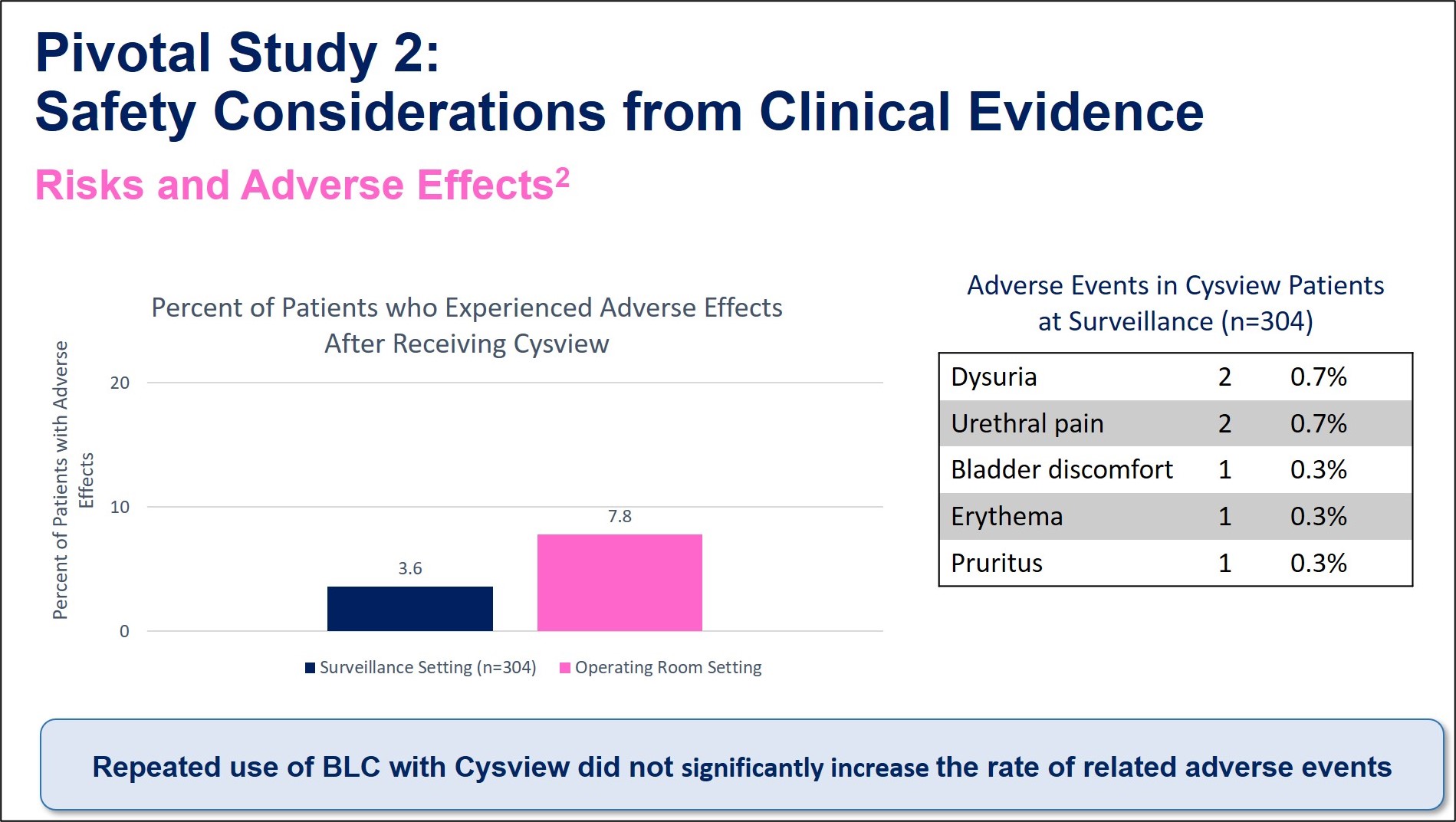
1 Stenzl A, Burger M, Fradet Y, et al. Hexaminolevulinate Guided Fluorescence Cystoscopy Reduces Recurrence in Patients with Nonmuscle Invasive Bladder Cancer. J Urol. 2010;184(5):1907-1914.
2 Daneshmand S, Patel S, Lotan Y, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Blue Light Flexible Cystoscopy with Hexaminolevulinate in the Surveillance of Bladder Cancer: A Phase III, Comparative, Multicenter Study. J Urol. 2018;199(5):1158-1165.


